Web服务器如Nginx,Apache的access_log一般都包括了很多关键信息,可以用于性能分析或者运营分析,CentOS 7的EPEL源集成了一个非常好用access_log分析工具goaccess,本文主要记录了如何使用goaccess进行nginx的日志分析:
安装
#安装epel源
yum install epel-release && yum -y update
#安装goaccess
yum install -y goaccess
配置
Nginx的log文件默认存放在/var/log/nginx/access_log, 基本的用法如下:
goaccess /var/log/nginx/access-log
第一次使用goaccess的时候,会弹出下面的对话框,要求配置access_log的时间和日志格式, nginx默认的日志格式就是NCSA, 所以一般就选第一个就可以了,然后goaccess在分析完成后会在终端上显示分析结果。

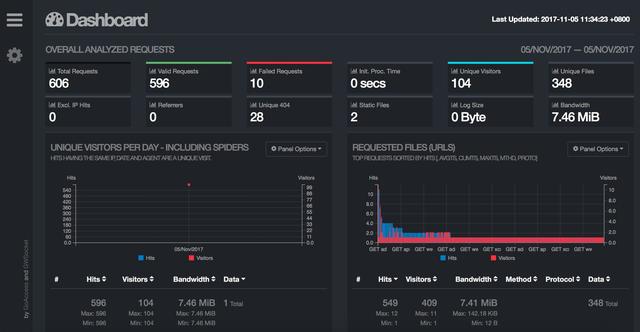
Goaccess还可以生成html格式的报表,有点可惜的是,目前好像仅支持English,命令也非常简单:
goaccess /var/log/nginx/access_log > goaccess.html
最后生成的报表包括pv, hits, agents等各种统计:
高级用法
Goaccess也支持日志定制,比如现在绝大部分nginx可能都会包括vhost,即一个物理nginx服务器可以支持多个域名的虚拟主机,但是nginx默认的NCSA日志格式在/etc/nginx/nginx.conf中配置如下,不包括vhost字段, 所以我们就无法在报表中区分不同虚拟主机的请求:
log_format main \
'$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" ';
为了支持vhost,我将nginx的log_format定制成下面这个样子, 主要是添加了$server_name字段用来显示vhost, 还有末尾的$xxx_time, 用来显示每个请求的耗时:
log_format main \
'[$time_local] $remote_addr $server_name "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" '
'$upstream_addr $request_time $upstream_response_time';
为了让goaccess能适配这个格式,需要将/etc/goaccess.conf中修改成如下格式:
#NCSA Combined Log Format
#
log-format %^[%d:%t %^] %h %v "%r" %s %b "%R" "%u"
其中,具体的指示符号可以参考goaccess的官方文档, 比如%^,代表忽略对应的字段:
SPECIFIERS
-
%x A date and time field matching the time-format and date-format variables. This is used when a timestamp is given instead of the date and time being in two separate variables.
-
%t time field matching the time-format variable.
-
%d date field matching the date-format variable.
-
%v The server name according to the canonical name setting (Server Blocks or Virtual Host).
-
%e This is the userid of the person requesting the document as determined by HTTP authentication.
-
%h host (the client IP address, either IPv4 or IPv6)
-
%r The request line from the client. This requires specific delimiters around the request (single quotes, double quotes, etc) to be parsable. Otherwise, use a combination of special format specifiers such as %m, %U, %q and %H to parse individual fields.
-
Note: Use either %r to get the full request OR %m, %U, %q and %H to form your request, do not use both.
-
%m The request method.
-
%U The URL path requested.
-
Note: If the query string is in %U, there is no need to use %q. However, if the URL path, does not include any query string, you may use %q and the query string will be appended to the request.
-
%q The query string.
-
%H The request protocol.
-
%s The status code that the server sends back to the client.
-
%b The size of the object returned to the client.
-
%R The “Referer” HTTP request header.
-
%u The user-agent HTTP request header.
-
%D The time taken to serve the request, in microseconds.
-
%T The time taken to serve the request, in seconds with milliseconds resolution.
-
%L The time taken to serve the request, in milliseconds as a decimal number.
-
%^ Ignore this field.
-
%~ Move forward through the log string until a non-space (!isspace) char is found.
-
~h The host (the client IP address, either IPv4 or IPv6) in a X-Forwarded-For (XFF) field.
Goaccess还可以从管道支持输入,这样可以做一些更灵活的处理,比如,access_log日志中的request字段并不包括server_name, 为了让request能够包含完整的url, 我们可以用下面的命令,因为awk的第4列包含了server_name, 这个命令将server_name放到了request的前面组成了完整的url,再用作goaccess的输入:
awk '$6=$4$6' access.log | goaccess -a -